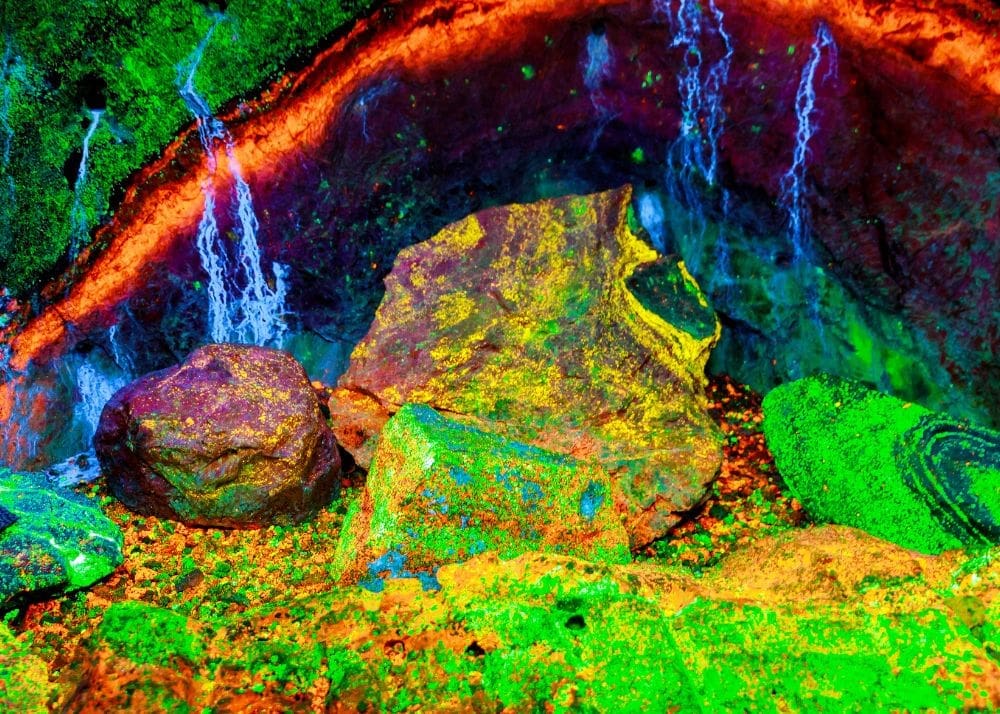
Ultraviolet Mineral Identification: A Practical Guide
Introduction: The Practicality of Ultraviolet Mineral Analysis
The identification of ultraviolet minerals is an essential process for geologists and enthusiasts alike, enabling the observation of unique characteristics that are not visible under normal lighting conditions. This article outlines the methodology and tools used for ultraviolet mineral identification.
Understanding Ultraviolet Light in Mineralogy
Ultraviolet light, divided into long-wave and short-wave, is the cornerstone of ultraviolet mineral identification. The type of UV light used can influence the visible response in minerals, which is crucial for accurate identification and analysis.
Mineral Responses to UV Light
Ultraviolet minerals react distinctively to different wavelengths, with some showing variation in color. An example is Texas calcite, which appears pink under long-wave UV light and blue under short-wave UV light.
Portable UV Lamps in Mineral Identification
The advent of portable ultraviolet lamps has made the observation of ultraviolet minerals more accessible. These lamps often allow users to switch between long-wave and short-wave UV light, catering to the needs of various mineral types.
Safety Measures with UV Equipment
When using UV lamps, it is crucial to take safety precautions due to the heat emitted by certain bulbs, such as argon bulbs and hot bulbs. Proper usage ensures both personal safety and the integrity of the mineral specimens.
Summary Table of UV Mineral Characteristics
The following table provides a quick reference for the interaction of ultraviolet minerals with UV light:
| Feature | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Types of UV Light | Long-wave and short-wave, affecting mineral visibility. | – |
| Mineral Reaction | Minerals respond uniquely to UV light, affecting identification. | Texas calcite |
| Color Variation | Minerals can change color depending on the UV wavelength. | Pink to blue in varying UV light |
| Portable UV Lamps | Essential tools for field and lab identification. | – |
| Safety Precautions | Necessary due to the potential hazards of heat. | Argon bulb, Hot bulb |
Conclusion: The Importance of UV Mineral Identification
Ultraviolet mineral identification is a critical process that provides insights into the composition and properties of minerals. Utilizing UV light in a safe and informed manner allows for a deeper understanding of mineralogical specimens. For additional resources or to view a collection of ultraviolet minerals, visit Miamiminingco.com.
10 FAQs Ultraviolet Mineral Identification
- What is ultraviolet mineral identification? Ultraviolet mineral identification is a method used to observe and analyze the properties of minerals that fluoresce under ultraviolet (UV) light, revealing characteristics not seen in natural light.
- Why is UV light used to identify minerals? UV light is used because certain minerals have the ability to absorb UV radiation and emit visible light, a property known as fluorescence, which can aid in their identification.
- What are the types of UV light used in mineral identification? There are two main types of UV light used: long-wave and short-wave. Each type interacts differently with minerals, causing them to fluoresce in various colors.
- Can all minerals fluoresce under UV light? No, not all minerals fluoresce. The ability to fluoresce depends on the mineral’s composition and structure. Only specific minerals will show fluorescence when exposed to UV light.
- What are some examples of minerals that fluoresce under UV light? An example provided in the article is Texas calcite, which fluoresces pink under long-wave UV light and blue under short-wave UV light.
- How do portable UV lamps work for mineral identification? Portable UV lamps emit UV light and can often switch between long-wave and short-wave light. This allows geologists and hobbyists to observe the fluorescent properties of minerals in the field or laboratory.
- What safety precautions should be taken when using UV lamps? Users should avoid direct skin or eye exposure to UV light, wear protective gear, and be cautious of the heat generated by certain UV lamps, especially hot bulbs.
- What is a hot bulb, and why is it considered dangerous? A hot bulb is an inexpensive UV light source that produces long-wave rays and can generate excessive heat, which may pose burn risks or cause damage to sensitive minerals.
- How can I learn which minerals are likely to fluoresce? Reference books, mineral databases, and academic papers often list the fluorescent properties of minerals. Experienced collectors and mineralogists can also provide insights.
- Where can I see examples of ultraviolet minerals? Examples of ultraviolet minerals can be viewed online at educational sites, such as Miamiminingco.com, or in person at museums, universities, or specialized mineral shows.